The Complete Guide to HJT Technology
The Complete Guide to HJT Technology
HJT, or Heterojunction Technology, is an innovative approach to solar cell technology that has gained attention in recent years due to its potential for high efficiency and improved performance. In this complete guide to HJT technology, we will cover what HJT is, how it works, its advantages and disadvantages, and its applications.
Table of Contents:
1. Introduction to HJT Technology
l What is HJT Technology?
l Historical Background
2. How HJT Technology Works
l HJT Solar Cell Structure
l Principle of Operation
3. Advantages of HJT Technology
l High Efficiency
l Better Temperature Performance
l Reduced Light-Induced Degradation (LID)
l Aesthetically Pleasing Design
4. Disadvantages of HJT Technology
l Complex Manufacturing
l Higher Initial Costs
l Sensitive to Shading
5. Applications of HJT Technology
l Residential Solar Panels
l Commercial and Industrial Solar Installations
l Utility-Scale Solar Farms
6. Future Developments in HJT Technology
l Tandem Solar Cells
l Bifacial HJT Cells
l Improved Materials and Manufacturing Processes
7. Conclusion
Now, let's delve into each section in detail:
1. Introduction to HJT Technology:
What is HJT Technology?
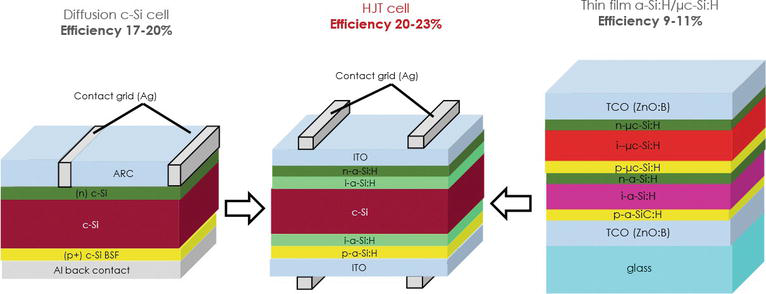
HJT (Heterojunction Technology) is a type of solar cell technology that combines the benefits of crystalline silicon solar cells with thin-film solar cells to achieve higher efficiency and improved performance.
Historical Background:
Provide a brief historical overview of the development and adoption of HJT technology.
2. How HJT Technology Works:
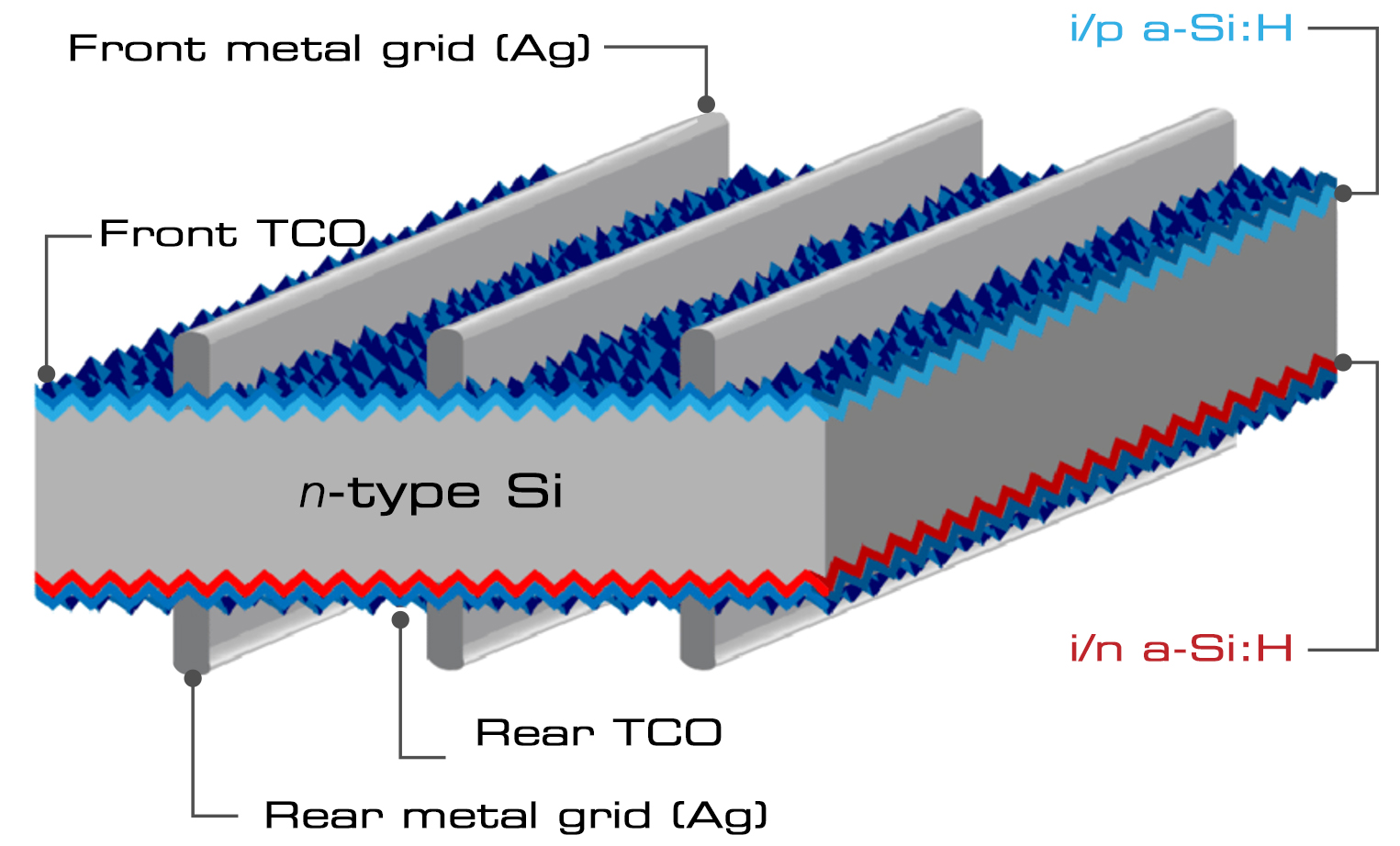
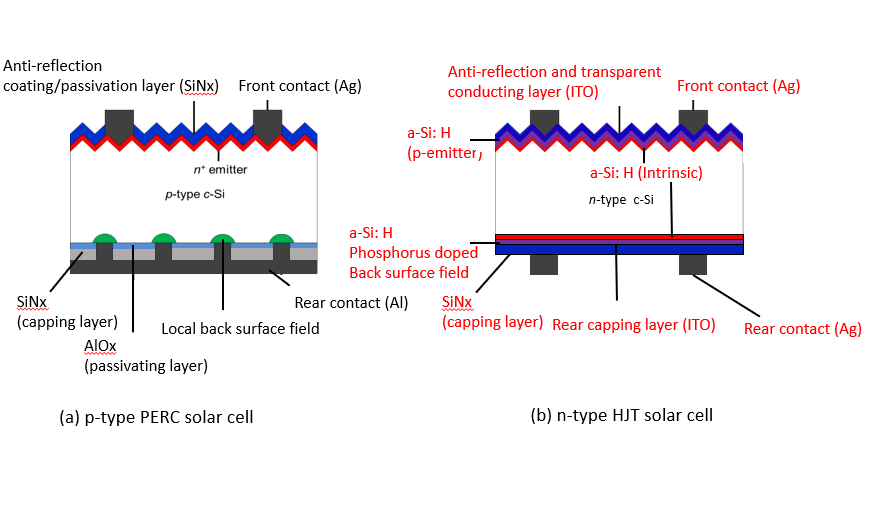
HJT Solar Cell Structure:
Explain the structure of an HJT solar cell, highlighting the key components that differentiate it from traditional silicon solar cells.
Principle of Operation:
Describe how HJT solar cells generate electricity from sunlight and why they are more efficient.
3. Advantages of HJT Technology:
High Efficiency:
Discuss the significant advantage of HJT technology in terms of energy conversion efficiency.
Better Temperature Performance:
Explain how HJT cells maintain higher efficiency at elevated temperatures.
Reduced Light-Induced Degradation (LID):
Highlight the reduced susceptibility to LID, which can be a concern in traditional solar cells.
Aesthetically Pleasing Design:
Mention the aesthetic appeal of HJT panels due to their uniform black appearance.
4. Disadvantages of HJT Technology:
Complex Manufacturing:
Discuss the challenges associated with the more complex manufacturing process of HJT cells.
Higher Initial Costs:
Explain why HJT panels tend to be more expensive initially.
Sensitive to Shading:
Address the sensitivity of HJT panels to shading and the impact on their performance.
5. Applications of HJT Technology:
Discuss how HJT technology is used in residential, commercial, and utility-scale solar installations, and mention any specific advantages in these applications.
6. Future Developments in HJT Technology:
Explore potential advancements and trends in HJT technology, such as tandem solar cells and bifacial HJT cells, as well as ongoing research and development efforts.
7. Conclusion:
Summarize the key takeaways from the guide, emphasizing the role of HJT technology in advancing the efficiency and performance of solar energy systems.
By the end of this guide, readers should have a comprehensive understanding of HJT technology, its benefits, drawbacks, and its potential to play a significant role in the renewable energy landscape.
